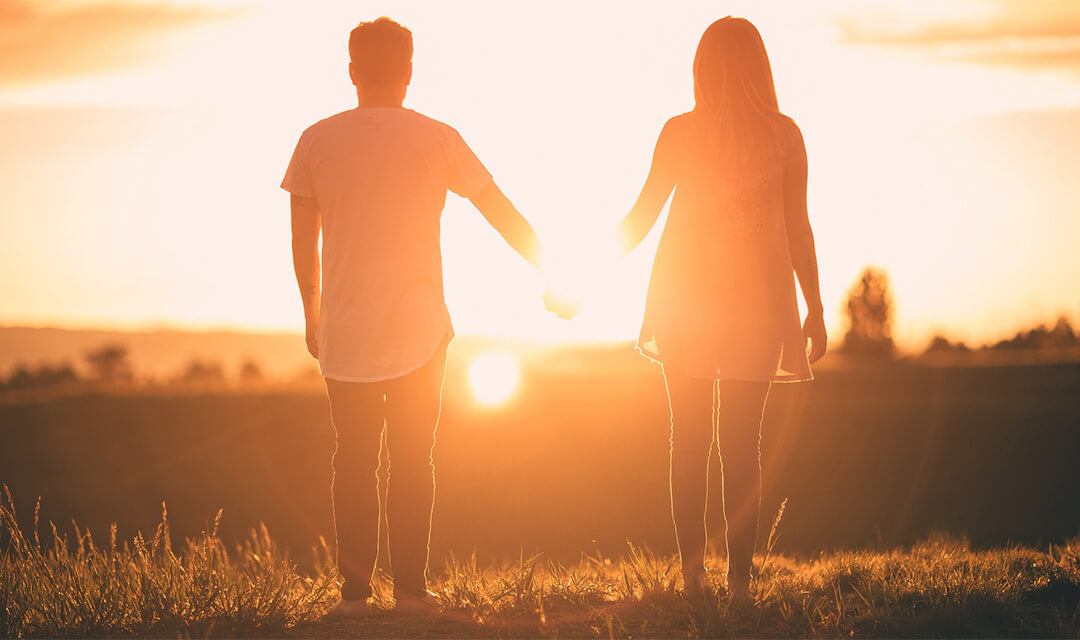
结婚该不该要嫁妆?
{{$t("details-view", {value: 276})}}
{{$t("details-like", {value: 22})}}
{{$tm("time")}}
{{ativityData.ativityTimeEn}} {{ativityData.ativityTime}}
{{$tm("location")}}
{{$tm("details-free")}}
¥ {{priceInterval.Highest}}
¥ {{priceInterval.Lowest}}
- {{priceInterval.Highest}}
{{MemberCoupon.value}}
「{{item.Title}}」{{item.couponDescs}}
{{$tm("details-about-event")}}
{{$t("details-event-consultation")}}
{{$t("details-event-consult2")}}
{{$t("No-comments")}}
{{$tm("details-registration-instructions")}}
{{$t("disclaimer1", {value: "翰墨青锋"})}}
{{$t("disclaimer2")}}
{{$t("disclaimer3")}}
{{$tm("report")}}